
C3d
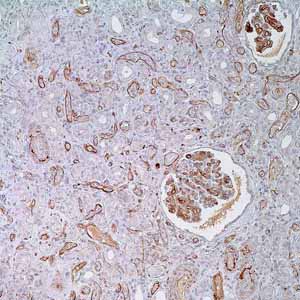
Complement component C3 plays a central role in the activation of the complement system. Its activation is required for both classical and alternative complement activation pathways. C3d deposition in the renal transplant peritubular capillaries (PTC) is indicative of acute rejection (AR) with subsequent high probability of graft loss. Anti-C3d, combined with anti-C4d, can be utilized as a tool for diagnosis of AR and to warrant prompt and aggressive anti-rejection treatment1,2,3.
In another study, Pfaltz et al. have shown that anti-C3d labeled the epidermal basement membrane in 97% (31/32) cases of bullous pemphigoid (BP), with none of the normal controls demonstrating such findings. In the same study 27% (3/11) cases of pemphigus vulgaris (PV) demonstrated intercellular C3d deposition4. Anti-C3d immunohistochemistry is a helpful adjunct in the diagnosis of BP (and perhaps PV), especially in cases where only formalin-fixed, paraffin- embedded tissue is available for analysis.
