
CD14 (EPR3653)
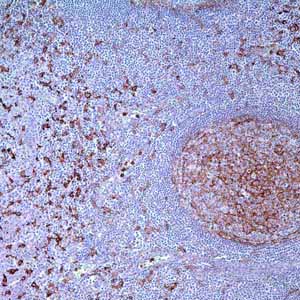
Anti-CD14 labels a 55 kDa, glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-linked membrane protein, involved in endotoxin binding and recognition of apoptotic cells.1 CD14 is expressed by monocytes and dermal dendritic cells; anti-CD14 is considered to be a macrophage-derived monocyte marker.2 CD14 is also present in granulocytes, endothelial, epithelial cells, and placental trophoblasts.3 In the spleen, CD14 can be expressed in the red pulp and marginal zone cells, and histiocytes around sheathed capillaries. In the lymph node, true sinusoidal histiocytes, and follicular dendritic cells stain with anti-CD14.3-7 However, other monocyte-derived cells in the lymph node, such as in sinusoidal histiocytosis with erythrophagocytosis, macrophages associated with anthracosis, germinal center tingible body macrophages in reactive germinal centers do not express CD14 antigen. CD14 is not expressed in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Anti-CD14 positive histiocytes are reported as markedly increased in DLBCL, but not in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), or follicular lymphoma (FL).7 Anti-CD14 is useful in identifying massive lymphadenopathy with sinus histiocytosis (Rosai-Dorfman disease) when used in a panel including anti-S100 and anti-CD68.8 Anti-CD14 can also be used for decalcified bone marrow biopsy specimens to show increased myelomonocytic and monocytic neoplastic cells in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and monocytic leukemia, and is very helpful in the distinction of myeloproliferative neoplasms, myelodysplastic syndrome, and acute monocytic leukemia. This antibody is more sensitive for leukemic monocytic cells than antibodies directed against CD163 and CD68/PG-M1.9
