
CD21 (2G9)
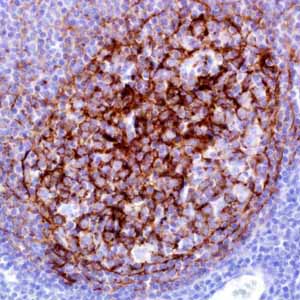
CD21 (also known as complement receptor 2 (CR2), C3d receptor, or EBV receptor) is a 140 kDa membrane protein on B-lymphocytes to which the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) binds during infection of these cells.1 The antigen is absent on T-lymphocytes, monocytes, and granulocytes.2,3
Anti-CD21 is useful in the identification of follicular dendritic cell matrix found in normal lymph node and tonsillar tissue. This antibody also labels follicular dendritic cell sarcomas.2,4,5 Anti-CD21 is valuable in differentiating follicular lymphoma with marginal zone differentiation from marginal zone lymphoma with follicular involvement. It also plays a role in distinguishing among nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma, lymphocyte-rich classic Hodgkin lymphoma, and T-cell/histiocyte-rich B-cell lymphoma in combination with other B-cell and T-cell markers.6 Anti-CD21 is also useful in identifying abnormal follicular dendritic cell pattern in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma and follicular T-cell lymphoma.7
