
Desmoglein 3 (EP306)
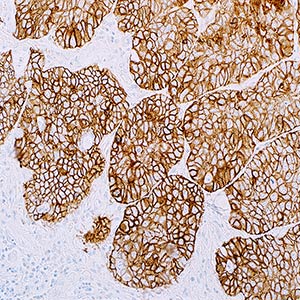
Desmosomes are cell to cell adhesion complexes that provide mechanical integrity to keratinocytes by linking to keratin intermediate filaments.1,2 Desmosomes are made up of two major transmembrane proteins known as desmoglein (DSG) and desmocollin.1 Three DSG subfamily members have been identified-DSG1, DSG2, and DSG3-and are part of the cadherin cell adhesion molecule superfamily. DSG3 makes up the calcium binding transmembrane glycoprotein component of desmosomes in vertebrate epithelial cells.2 DSG3 is found in both the basal and suprabasal layers of the stratified epithelia. DSG3 has been found to be expressed in 85-99% of squamous carcinomas of the lung and in only 0-2% of adenocarcinomas in the lung.1 In a study performed by Tacha et al. DSG3 labeled 0/115 lung adenocarcinomas.2 In another study performed by Huang et al. it was found that DSG3 was expressed in 90% of pure squamous cell carcinomas in the bladder. In urothelial carcinomas with squamous differentiation DSG3 labeled 79% of tumors in the squamous component and 9% in the urothelial component. This corresponded to a sensitivity and specificity of 86% and 91% respectively for DSG3.1 DSG3 is reliable marker for differentiating lung squamous cell carcinoma from lung adenocarcinoma. DSG3 is also a highly specific marker for labeling squamous differentiation and can be used to help identify a squamous component in urothelial carcinomas.1
