
EGFR (SP84)
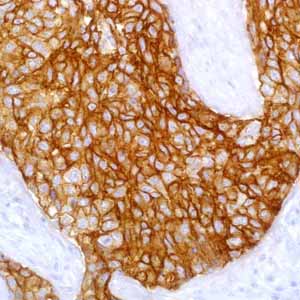
EGFR is a 170-kDa transmembrane glycoprotein encoded by the HER-1 proto-oncogene located at 7p11.2-p12.1-2, EGFR is widely expressed on the surface of epithelial cells, fibroblasts, gliocytes, keratinocytes, and other cell types.1 EGFR is overexpressed in many epithelial malignancies including carcinomas of the colorectum, stomach, esophagus, pancreas, oropharynx, adrenocortical carcinoma, non–small cell carcinoma of the lung, cutaneous and anal squamous carcinoma, and head and neck squamous carcinoma.1-5 EGFR protein expression has also been a common finding in breast carcinoma, particularly in triple-negative, basal-like breast carcinomas.4 Studies suggest that EGFR expression is not unique to carcinomas and may be present in malignant bone and soft tissue tumors.5 Soft tissue sarcomas such as synovial sarcoma and epithelioid sarcoma show morphologic and immunophenotypic features of epithelial differentiation. Hence, EGFR overexpression is often seen in synovial sarcoma and epithelioid sarcoma. IHC analysis of 48 synovial sarcoma specimens representing primary and metastatic lesions using the anti-EGFR antibody demonstrated positive reactions in 34 of 48 cases (71%). The same study included 32 cases of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, in which EGFR overexpression was found in 20 cases (62.5%).4 Cascio, MJ et al. found 13 of 15 cases (87%) of epithelioid sarcoma displayed immunoreactivity of EGFR by IHC. Findings included strong, homogenous staining in the majority of cases, but absence of either gene amplification or kinase domain mutations.5
