
Gastrin
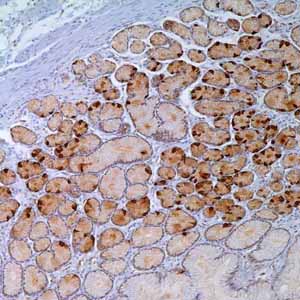
Gastrin is a hormone whose main function is to stimulate secretion of hydrochloric acid by the gastric mucosa, which results in gastrin formation inhibition. This hormone also acts as a mitogenic factor for gastrointestinal epithelial cells. Gastrin has two biologically active peptide forms: G34 and G17. They activate two different receptors: the CCK-1 receptor, which has low affinity for gastrin but high affinity for the related hormone cholecystokinin (CCK), and the CCK-2 receptor, which has high affinity for both gastrin and CCK and mediates the acid-secretory as well as the proliferative effects of gastrin. More recently, gastrin has been suggested to induce leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions and to have a pro-inflammatory effect. Anti-gastrin stains G-cells of human antral/pyloric mucosa and cells producing gastrin or a structural gastrin analog as is seen in stomach; no staining of other cells or tissue types has been observed. This antibody may react with sulfated and non-sulfated forms of gastrin.
