
GATA1 (4F5)
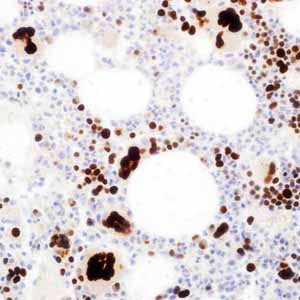
GATA-1 is a nuclear transcription factor that belongs to the family of GATA proteins which bind the DNA sequence (A/T)GATA-(A/G) by a highly conserved zinc finger domain located on the X chromosome.1,2 GATA1 is expressed in the cells of the erythroid, megakaryocytic and mast cell lineages and is found in low levels in multipotential and Sertoli cells of the testis.1 GATA1 normally suppresses the proliferation of megakaryocytic and erythroid precursors while promoting their differentiation. GATA-1 is crucial for normal erythroid and megakaryocytic development. Missense mutations in GATA1 in humans causes a familial dyserythropoietic anemia and thrombocytopenia. GATA1 has been implicated in childhood acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL) and transient myeloproliferative disorder in children with Down syndrome (DS). Acquired mutations in exon 2 of GATA1 an X-linked gene has been described in DS patients with AMKL.2 Anti-GATA1 can be used to identify megakaryocytes, erythroid precursors and megakaryocytic malignancies.1, 2
