
Synaptophysin
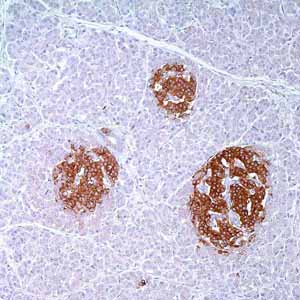
Anti-synaptophysin reacts with neuroendocrine cells of human adrenal medulla, carotid body, skin, pituitary, thyroid, lung, pancreas, and gastrointestinal mucosa. Positive staining is seen in neurons of the brain, spinal cord, retina, Paneth cells in the gastrointestinal tract, and gastric parietal cells. This antibody identifies normal neuroendocrine cells and neuroendocrine neoplasms. Diffuse, finely granular cytoplasmic staining is observed, which probably correlates with the distribution of the antigen within neurosecretory vesicles. The expression of synaptophysin is independent of the presence of NSE or other neuroendocrine markers. Anti-synaptophysin is an independent, broad-range marker of neural and neuroendocrine differentiation.
